Management Specification for Test Samples and Blocks
1.Purpose
To ensure timely provision of test specimens that meet relevant standard requirements to the spectral analysis laboratory and mechanical testing laboratory, this specification is formulated.
2. Responsibilities
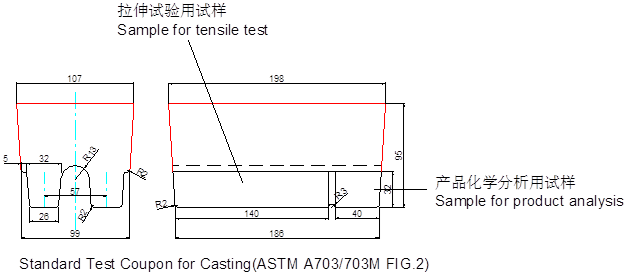
2.1 The Minister of Biotechnology is responsible for the design of test block patterns and molds to ensure that the size of the test blocks continues to meet relevant standards or customer requirements. The size of the sand casting test block is shown in the attached figure
2.2 The sand casting modeling team leader is responsible for scheduling the production of sand casting test blocks and ensuring that the relevant markings meet the requirements.
2.3 The gas welding team leader is responsible for the post-processing and heat treatment of the test blocks, ensuring that the test blocks with qualified external dimensions and heat treatment that meets the process requirements are provided within the specified time.
3. Scope
This scope applies to all pressure bearing valve castings manufactured in the factory, including the body, valve plate, and upper valve cover.
4. Production requirements
4.1 Test block size
The test block mold is made according to the general requirements for cast steel parts for pressure parts in ASTM A703/703M, and the detailed dimensions are shown in the attached figure.
Ensure that the test block can meet the processing requirements of both ASTM A370 and JIS Z 2201 standard specimens simultaneously.
Ensure that one test block can produce two tensile specimens or four impact specimens.
4.2 Quantity of test blocks
Conventional materials, one sample is made for each melting furnace.
Low temperature cast steel (as shown in Table 1) or materials with special requirements (specified by the customer), two test blocks are made for each melting furnace, one for processing tensile specimens and one for processing impact test specimens.
| ASTM | LCB | LCC | LC1 | A352-LC2 | LC3 |
| JIS | SCPL1 | —— | SCPL11 | SCPL21 | SCPL31 |
4.3 Sample production requirements
Sand casting: Molding worker determines the number of test blocks based on the material and output (number of furnaces) scheduled for the day.
Marking: The wooden mold worker placing material, furnace number, and other casting characters at the bottom of the test block, as shown in Figure 1:
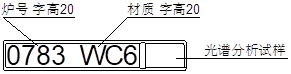
After the pouring is completed, the test blocks are placed in zones according to the furnace number. The precision casting and polishing team leader arranges the cleaning of the test blocks and stamps the material and furnace number on the test blocks based on the casting records (refer to Figure 1).
4.4 Post processing
4.4.1 Collection of test blocks
4.4.1 The test blocks cast the previous night need to be cleaned and cut within three working days, and are the responsibility of the precision casting and polishing team leader and the gas welding team leader.
4.4.2 Spectral analysis sampling
The gas welding team leader will hand over the collected test blocks to the spectral analyzer for sampling, and the analyzer will cut and sample according to the cutting marks on the test blocks. Return the remaining sample to the gas welding team leader.
4.4.3 Heat treatment
The sample should be subjected to heat treatment using the same process as the casting it represents in the heat treatment furnace. The gas welding team leader is responsible for filling in the relevant information (furnace number, material quantity, process requirements) on the document. After heat treatment, check the documents for any errors.
4.4.4 Test Sample placement
Set the sample placement area and arrange them in the order of furnace numbers.
4.4.5 Preservation of test blocks
Two small test pieces can be cut from one test piece, with one piece processed into a tensile specimen (or impact specimen) and the remaining piece kept as a backup. The backup retention period is one year.
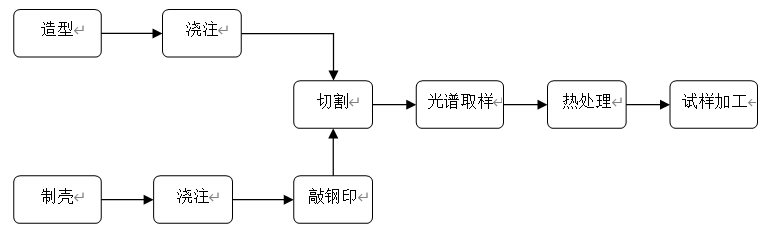
5. Control flowcharts
Refer to Figure 2:
Guokun Casting, of Baoding Hebei is an ISO 9001-2008 registered iron and steel foundry & supplier of high quality carbon steel, cast iron and machined castings used in power, mining, railway, agricultural, tillage, truck, automobile, pump, valve, motor, pipe fittings and gear industry. With a montly capacity of 10,000kgs and with more than 15 years of experience ensure the short delivery and the highest valued iron & steel casting parts.
Casting Process we offered:
| No. | Investment Casting | Sand Casting | Centrifugal Casting | Precision Machining |
| Process | Investment casting, also named lost-wax casting, making parts from molten metal. | Sand casting, the most widely used casting process, utilizes expendable sand molds to form complex, metal parts that can be made of nearly any alloy | Centrifugal casting, sometimes called rotocasting, is a metal casting process that uses centrifugal force to form cylindrical parts | Precision machining from the tubes, bars, blocks to get the required shapes. |
| Metal | steel, brass, copper and bronze | steel, brass, copper and copper, cast iron | Brass, bronze and copper alloy | steel, brass, copper and bronze, aluminum, etc |
| Weight | Max. 500kgs | Max. 20,000kgs | Max. 10,000 kgs | Max. 10,000 kgs |
| Tolerance | CT4-7 | CT9-CT12 | as per drawings | as per drawings |
| Advantage | Complex structure and high production rate | Can produce complex structure | Fine inner structure No defects like sand casting | high precision |